了解全新试剂盒


什么是 PureTarget?
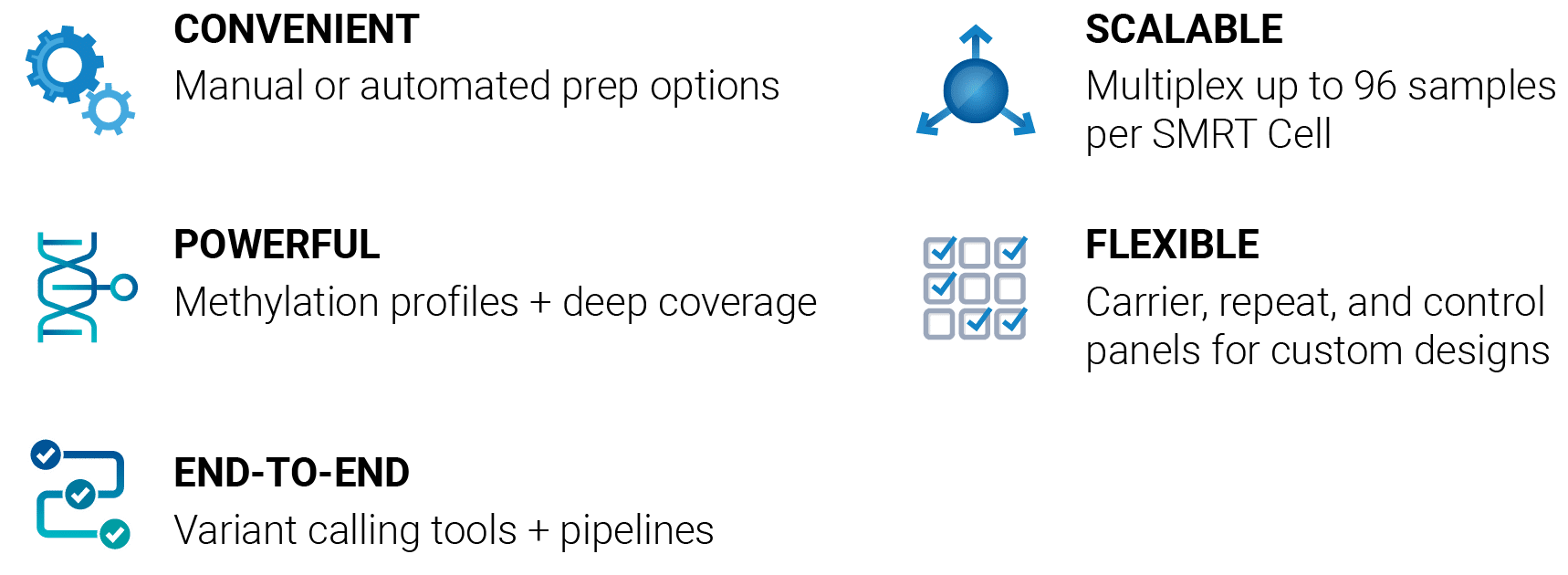
PureTarget 利用CRISPR-Cas9系统生成靶向天然DNA文库。这种无扩增方法保留了如甲基化等表观遗传信号,并避免了PCR伪影。 通过简化的工作流程、可扩展的多重检测能力以及对困难区域的高深度覆盖,PureTarget panel可替代多种检测方案,使实验室能够单次检测即可分析FMR1、FXN、F8和SMN1等具有挑战性的基因位点。
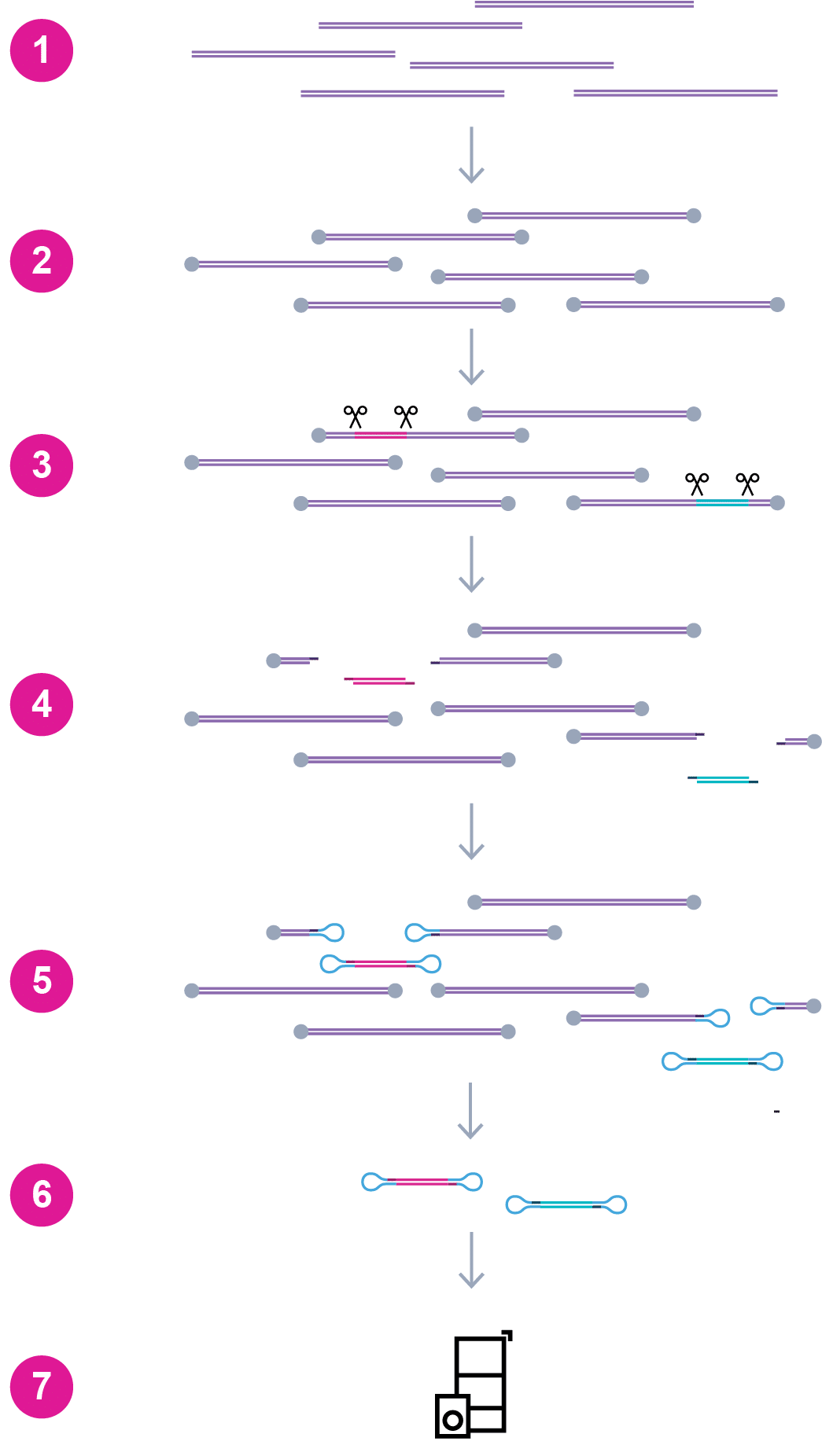
Amplification-free target enrichment workflow
- Start with high molecular weight DNA extracted from human blood or lymphoblastoid cells with Nanobind kits
- Dephosphorylate to block DNA ends
- Cut DNA with Cas9 and pair of guide RNAs on each side of target
- Add dA tail
- Ligate indexed SMRTbell adapters
- Remove non-SMRTbell templates with nuclease digestion
- Pool and sequence 96 samples on Revio + SPRQ with automation kit (8-48 samples on Vega or Revio + SPRQ with manual kit)
Puretarget Datasets
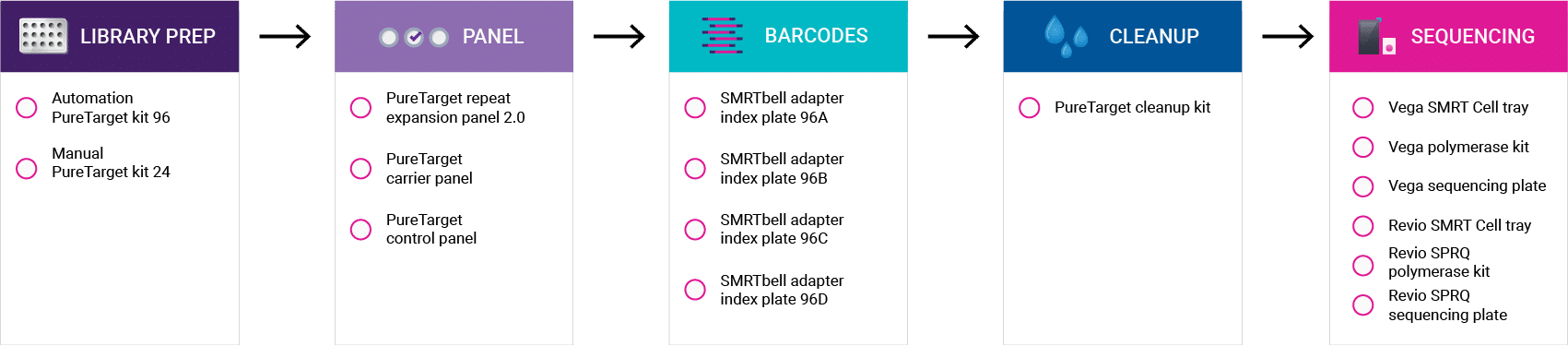
PureTarget 试剂购买指南
模块化组合在产品内容和规模上提供灵活性。
PureTarget FAQs
PureTarget 采用无扩增技术,因此其最佳应用场景包括:
· 难以扩增的区域,例如串联重复序列或GC富集序列
· 甲基化或单倍型分析至关重要的靶标
· 具有高序列同源性或存在大结构变异的基因
PureTarget 的其他优势包括:
· 提供用于 Hamilton NGS STAR 自动化平台的 PureTarget 96 试剂盒自动化脚本,周转时间为 16 小时
· 手动操作的 PureTarget 24 试剂盒,周转时间为 8 小时
· 能够将多种类型的挑战性靶标(如串联重复扩展、倒位、大片段缺失)整合到一个面板中
· 为重复扩展面板和携带者筛查面板提供相应的变异检测软件流程
没问题!您可以通过屏蔽不需要的靶标来创建计算机模拟(虚拟)面板。 只需在 SMRT Link 软件中使用”靶向富集”或”PureTarget 重复扩展”分析模块进行分析之前,修改您的 BED 文件以移除不需要的靶标即可。输出文件中将只包含 BED 文件中所列基因座的数据。
官方支持的样本类型是通过 Nanobind 提取的人体血液、淋巴母细胞和唾液(仅支持手动文库制备和 Revio SPRQ 测序试剂板),或者来自 Coriell 研究所的、质量数值为 30 kb > 5 的淋巴母细胞 DNA。使用这些样本可获得 PureTarget 的最佳性能。关于将 Nanobind 与您的 PureTarget 试剂盒捆绑订购的事宜,请咨询您当地的销售代表或联系 support@pacb.com。 其他样本也与 PureTarget 兼容。欲了解更多信息,请参阅 Repeat Expansion app note.
Also available from the application kit consumables page under each panel kit and in the hosted datasets
这些坐标文件也可在 应用试剂盒耗材页面 上每个面板试剂盒的下方以及 托管的数据集 中找到
| CARRIER PANEL | |
|---|---|
| Gene | Disease |
| F8 | Hemophilia A |
| FXN | Friedreich ataxia |
| FMR1 | Fragile-X disease (FXS) |
| CYP21A2 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| TNXB | Classical-like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
| HBA1/2 | Alpha thalassemia |
| GBA | Gaucher |
| SMN1/2 | SMA |
| ARX | Early-infantile epileptic encephalopathy (EIEE1) and Partington syndrome (PRTS) |
| HBB | Sickle cell anemia and Beta thalassemia |
| RPGR | X-linked retinitis pigmentosa |
| AFF2 | Fragile X, FRAXE type |
| REPEAT EXPANSION PANEL 2.0 | |
|---|---|
| Gene | Disease |
| ATN1, ATXN1, ATXN2, ATXN3, ATXN7, ATXN8, ATXN10, CACNA1A, PPP2R2B, TBP, BEAN1, DAB1, FGF14, NOP56, ZFHX3 | Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) |
| FMR1 | Fragile-X disease (FXS) |
| AFF2 | Fragile X syndrome, FRAXE type |
| AFF3 | Intellectual disability associated with fragile site FRA2A |
| C9orf72 | Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
| FXN | Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) |
| RFC1 | Cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, and vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS) |
| NOTCH2NLC | Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease, Alzheimer disease and parkinsonism phenotype (NIID) |
| DMPK, CNBP | Myotonic dystrophy (DM) |
| HTT | Huntington disease (HD) |
| JPH3 | Huntington’s disease-like type2 (HDL2) |
| TCF4 | Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy 3 (FECD3) |
| AR | Kennedy Disease, Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy, (SBMA) |
| PABPN1 | Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) |
| ABCD3, GIPC1, LRP12, PILPL1 | Oculopharyngodistal myopathy (OPDM) |
| HOXD13 | Syndactyly (SD5) |
| PHOX2B | Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS) |
| PRNP | Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) |
| CSTB | Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsy Type 1 (EPM1) Unverricht-Lundborg Disease (ULD) |
| SAMD12 | Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy type 1 (FAME) |
UBL 4A
ACTB
GAPDH